Commercially available NF membranes are commonly acid sensitive, showing poor performance and stability in acidic wastewater treatment.
WD News: A research group led by Prof. Wan Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel catalytic template–assisted interfacial polymerisation strategy to prepare a highly permeable acid-resistant nanofiltration (NF) membrane for acidic wastewater treatment. The study was published in the AIChE Journal.
This type of membrane shows high permeation for H+ while maintaining high retention for organics, which is beneficial to realising “zero discharge” in strongly acidic organic wastewater reclamation.
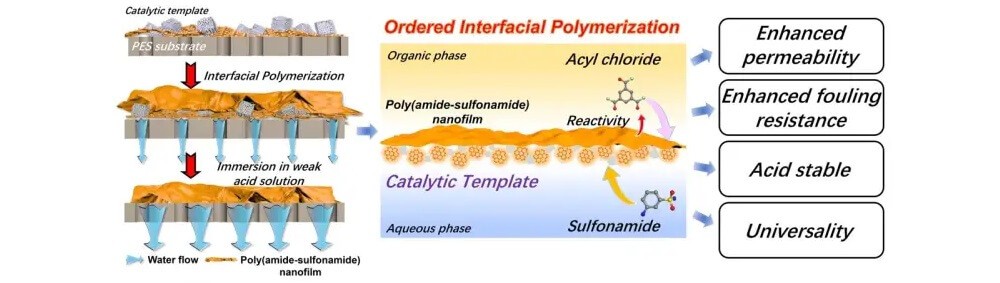
Due to the low reactivity of acid-stable monomers, current acid-resistant NF membranes have extremely low permeability and low separation selectivity for H+/organics.
The researchers attempted to boost membrane permeability and improve separation layer homogeneity through a strategy to increase separation selectivity for H+/organics.
They synthesised aminopyridine-doped graphene quantum dot acylation catalysts, which co-loaded with ZIF-8 nanoparticles by in-situ growth as a sacrificial template on a porous substrate. Then the 3-aminobenzenesulfonamide with strong conjugation effect was selected as the aqueous monomer to react with trimesoyl chloride to fabricate the acid-resistant poly(amide-sulfonamide) network.
Benefiting from increased monomer reactivity and optimised phase integrity, the resulting ultra-thin membrane showed excellent water permeance (20.4 Lm-2h-1bar-1) with Na2SO4 rejection of 90.5%.
Due to its acid stable polysulfonamide backbone, low layer thickness and narrow pore size distribution, the membrane exhibited pigment/H+ selectivity superior to the commercial GE Duracid membrane at 8 wt% H2SO4 condition, even for real cane molasses acidic wastewater.
“Combining a conventional acylation catalyst with a novel nanoparticle carrier, we developed a new scalable strategy for synthesis of special separation membranes,” said Prof. Luo Jianquan from IPE, corresponding author of the study. “Our work also offers a new horizon for utilising more monomers with special structure for synthesis of functional polymers via interfacial polymerisation method.”
Source: Chinese Academy of Sciences, Phys.org
Image courtesy: Pixabay, Chinese Academy of Sciences